How Do the Moon and Sun Affect the Tides?
There are many things humans can learn regarding how the moon and sun and weather affect the stability in the sea and ocean.
The moon is the primary factor that governs Earth’s tides. The moon’s gravitational force influences Earth’s low and high tides. But, how exactly does the moon affect the tides?
It is critical for readers (like you) to understand how the moon’s gravitational pull affects Earth’s oceanic tides. Knowing and understanding when to expect high and low tides can help boaters and fishermen stay safe on the water. Weather conditions (especially tides) are also important to consider when deciding when to go fishing.
The knowledge allows you to understand how neap tides, spring tides, and the entire tide cycle work, as well as what to expect at different times of the moon cycle.
The moon has a significant impact on the occurrence of the Earth’s tides. Furthermore, the sun exerts a significant influence on tidal forces. Solar tides are described as a variant of lunar tidal rhythms because they are roughly half as powerful as lunar tides. The two types of tides cannot be represented by two distinct sets of tidal patterns.
The sun, moon, and Earth are all aligned during the full or new moon phases. Solar tides supplement lunar tides at these times, resulting in an extra-low and high tide. Spring tides are both extremely high and extremely low tides.
After about a week, the moon and sun are at right angles to each other. During this time, the solar tides cancel out a significant portion of the lunar tides, resulting in moderate tides known as neap tides.

Every lunar month, two sets of spring and neap tides occur.
This article will walk you through the forces and circumstances that influence how the sun and moon affect tides on Earth’s oceans. Furthermore, the article aims to help you understand how tides can affect you while sailing on the ocean.
What is a Tide?
Most people are familiar with the ebb and flow of tides. Tides are the movements of oceanic waters that cause them to come in and go out. The coming in and going out may not be as quick as you believe. Tides can take a while, depending on the lunar cycle.
Science may not support the common understanding of how tides occur because, while it may appear that tides creep in and out on a regular basis, there is more to explain than meets the eye. Gravity is the primary influence on the occurrence of tides. Gravity causes the sea level to fall and rise at different times.
Tides are actually just vertical movements of seawater. A tide causes oceanic waters to move downward and upward, forward and backward.
Current is formed by the oceanic waters flowing out and in patterns. When the forming current floods, the tides rise, and when the current ebbs, the tides fall.
The two current patterns interact to produce the phenomena known as tides.
What Do the Tides Do?
The rising and falling movements of water caused by tides are extremely important for boaters. Your boat, without a doubt, floats on the water and controls the boat’s movement.
The rising water levels will most likely moor your boat, allowing you to sail through. The length of line you may need to use and how you dock your boat is highly dependent on the nature of the tides. You’d prefer it if the harbor was as shallow as possible.
How Does the Moon Affect the Tides?
The sun and moon work together to influence the tidal cycle of Earth’s oceanic life. Every day, the Earth’s oceans experience two high and two low tides. Between the high and low tides, the current continues to flow in.
But what factors influence the tides?
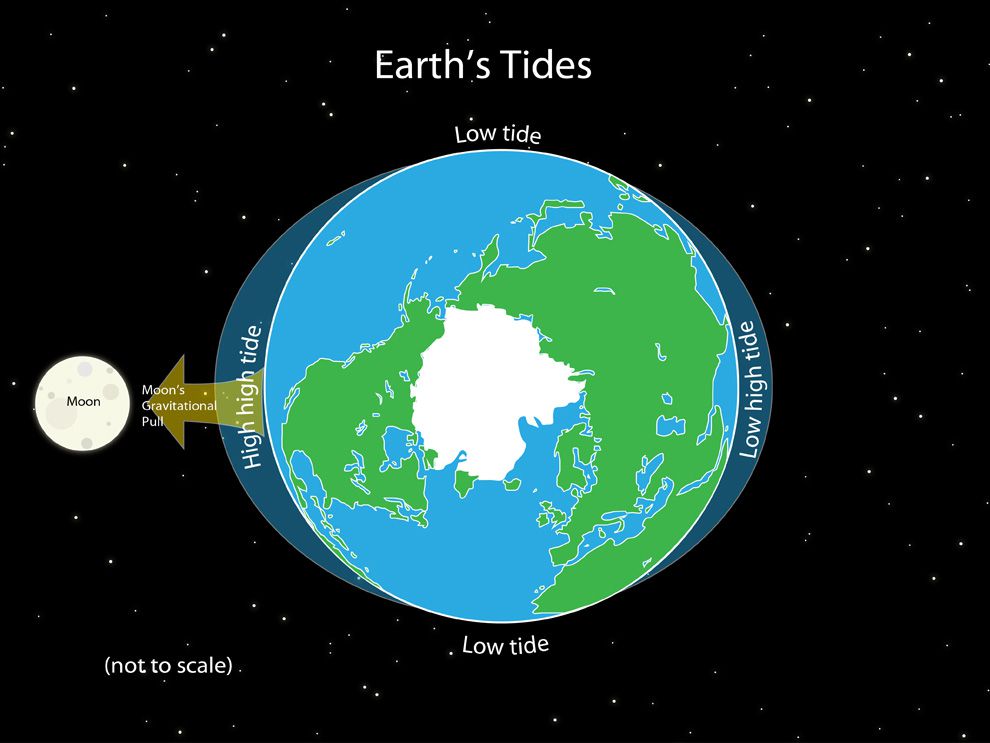
The moon’s gravitational force has the greatest influence on the occurrence of tides on Earth’s oceanic waters.
The moon’s gravitational force acts on the Earth, causing a tidal pull. The gravitational force of the moon causes the Earth to bulge towards the side closest to the moon. The opposite side of the Earth bulges as well, causing oceans to rise.
When the Earth bulges, the bulging side experiences high tides while the rest of the world experiences low tides.
You’re probably wondering how the sides closest to and farthest from the moon bulge and cause tides. To comprehend this phenomenon, imagine the Earth as a spherical object, such as a ball. The gravitational pull squeezes the ball-like object in the center.
As a result, the sides closest to and farthest from the moon bulge and form sharper ends, giving rise to tidal pulls.
Tidal forces are largely inconsistent as a result of coastline influences. Notably, the force created by the moon on one side of the globe may be significant in creating tides despite being barely visible on the other.
It’s worth noting that the moon’s gravitational pull is evenly distributed. The effect of this force, however, is erratic due to the contributions of the Earth’s coastlines.
What Does Science Say About the Influences of Tides?
The force of gravity is responsible for ocean tides. It is the attractive pull that all matter uses to attract another; this force is what holds all matter, including humans, to the Earth.
Every matter that makes up the Earth attracts one another, drawing itself into this single spherical globe that we call the Earth.
Without these external gravitational forces and other factors, the Earth would be otherwise smooth and spherical, and the oceanic waters would be still and constant in-depth at all points.
However, this is not the case because the moon has a gravitational pull on the Earth, affecting a portion of the Earth’s life, particularly the oceanic waters.
The oceanic tides are part of the scientific evidence that the moon exerts a gravitational force on the Earth, causing the Earth to bulge on both sides closest to and farthest from the moon.
Scientists contend that tides are higher where the ocean has bulged, both near the moon and on the opposite side of the Earth.
Tides, on the other hand, are low in other parts of the Earth because of the bulging caused by the moon’s gravitational pull.
The Earth’s position closest to the moon, according to some, changes due to rotation, so the bulging continues to move. As a result, every part of the sea continues to rise and fall as the bulging occurs whenever it passes the location of the moon.
Scientists believe that tides take about six hours to cycle from high to low. Within a 24-hour period, there are approximately two sets of high and two sets of low tides.
How Does the Moon and Sun Affect Tides?
The sun, in addition to the moon, influences tidal pulls on the Earth’s oceans. When the sun, moon, and Earth align, the sun exerts a gravitational force on the Earth as well. The moon’s and sun’s gravitational forces can combine to increase the strength of the tides.
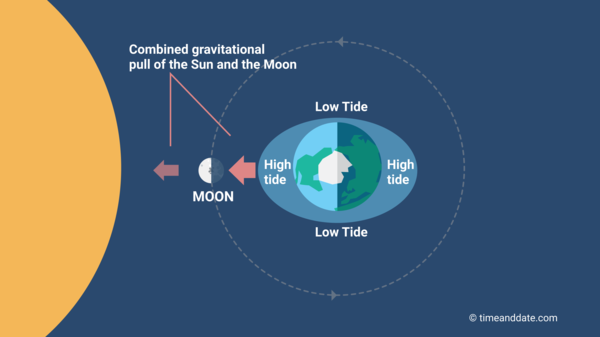
Furthermore, when the sun and moon are not aligned, the sun’s gravitational force opposes the moon’s, canceling some of the high tides and strengthening the low tides on the oceans. The valley and peak of the tides may be smaller than in the case of alignment at this point of gravitational cancelation.
Because of the other factors influencing the tides, the tidal pull processes may not be as simple as described in theory. Tidal processes may be complicated by factors such as coastlines, ocean shapes, and different ocean depths.
As a result, the oceanic waters splash in a way that causes the sea level to lower and rise by different amounts depending on your location. Locations in Canada, such as the Bay of Fundy, may experience changes in sea levels of up to 50 feet. Isn’t that incredible?
However, in most parts of the world, the variation of sea level amounts due to tidal pulls can be a few feet down and up with each low and high tide.
What are Other Factors Affecting Tides?
Apart from the effects of the moon’s and sun’s gravitational forces, systems also have an impact on the tides in the Earth’s oceans. When there is a strong wind blowing in the tide’s direction, the tide may appear to be stronger.
Floods can be caused by strong winds pushing tides further inland. However, it is unusual to have high tides and strong winds blowing in the same direction at the same time.
Winds blowing in the opposite direction of the low tides can also push the ebbing current and low tides further out into the sea. Winds’ effects may become more powerful than the moon’s gravitational force in such cases.

Furthermore, the occurrence of tides can be influenced by low and high-pressure systems. The amount of sea level in all areas is affected by pressure. As a result, pressure variations are more likely to influence changes in sea levels on oceans, thereby influencing tides.
Low tides can be caused by high pressure, while high tides can be caused by low pressure.
Types of Tides
- The Neap Tides
Alignments of bodies in the solar system can occur in some very unusual ways. In some cases, the sun and moon are at right angles to one another. The solar tides and the lunar tides are at odds right now.
The neap tides are formed as a result of this arrangement. Neap tides are the polar opposite of spring tides.
When the sun’s gravitational force and the moon’s gravitational pull are at right angles, they cancel each other out, resulting in the force having little effect on the Earth.
The result is higher low tides and lower high tides. It is worth noting that neap tides occur as frequently as spring tides.
- The Spring Tides
As previously stated in this article, both the moon and the sun influence the occurrence of tides. However, because the sun is farther away from the Earth than the moon, its effect on tides may be less than that of the moon.
Nonetheless, there will come a time in the solar system when the moon and sun will align. The effect on the tide is more noticeable than at any other time. The gravitational pulls of the sun and moon combine to cause tides on the sea.
Consequently, the occurrence of low and high tides happens due to solar tides and lunar tides interacting. These tides are known as spring tides. They are generally stronger than neap tides.
Spring tides usually form during the full or new moon. Spring tides are more powerful and occur every two weeks throughout the year.
What Do Tides Mean to Boaters?
Boaters must understand how tides work and when they are most likely to occur. Many people may not recognize the significance of understanding tide formation and effect until they are caught in them. You would be wise to read this article because it will undoubtedly assist you in understanding tides and their effects.

You will not overlook or regret learning about tides and how they work. The occurrence of tides, for example, can have an impact on the following:
- the length of anchor chains and dock lines that you may need during the tide
- a boat’s clearance under a bridge
- the manner in which you navigate inlets and channels. Tidal currents and depths can both impair your ability to navigate the ocean. You should be aware that you may not be able to navigate against some tidal currents, particularly in some channels.
- the length of time you can safely anchor in one location. Some boaters are beached without their knowledge during low tides. Furthermore, if you do not properly anchor your boat, high tides may send it adrift.
- How you clear your boat for the keel over debris or shoals. No boater wants to run aground.


